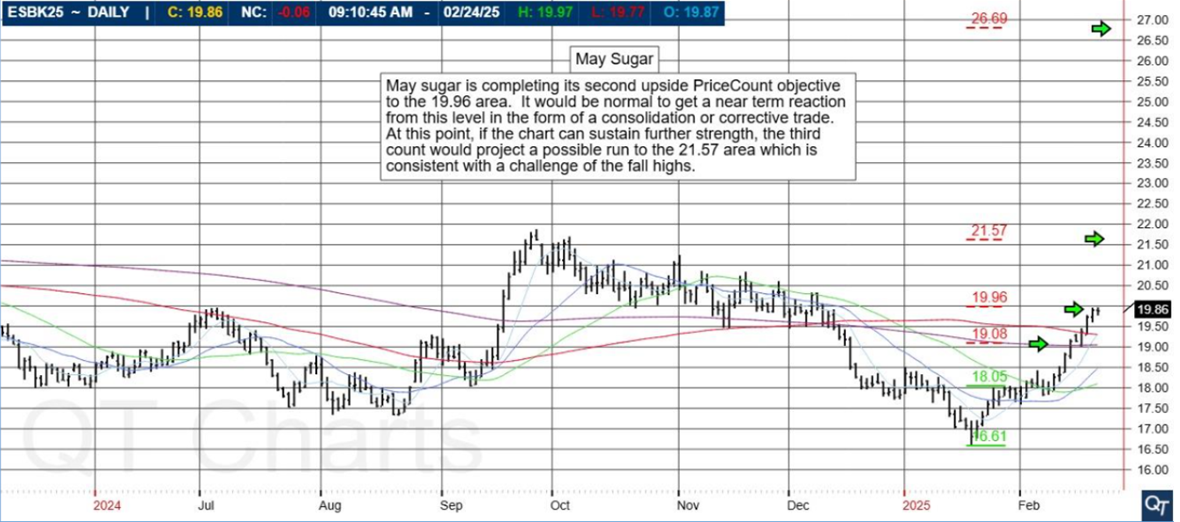
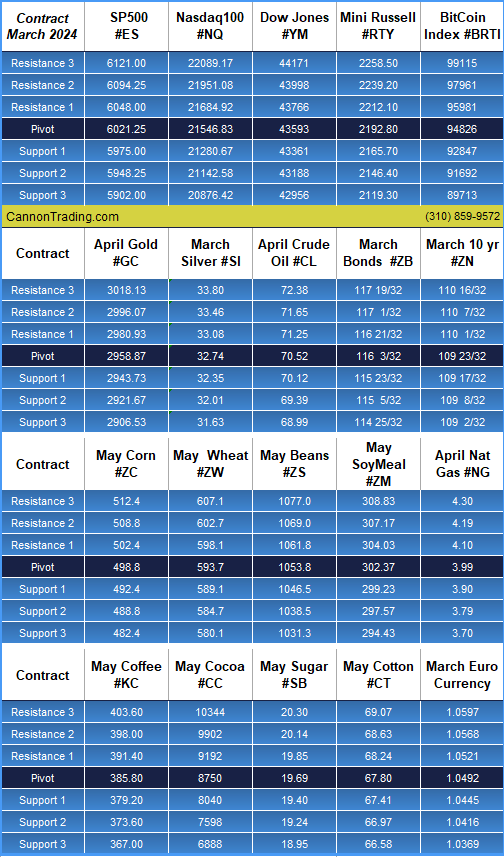
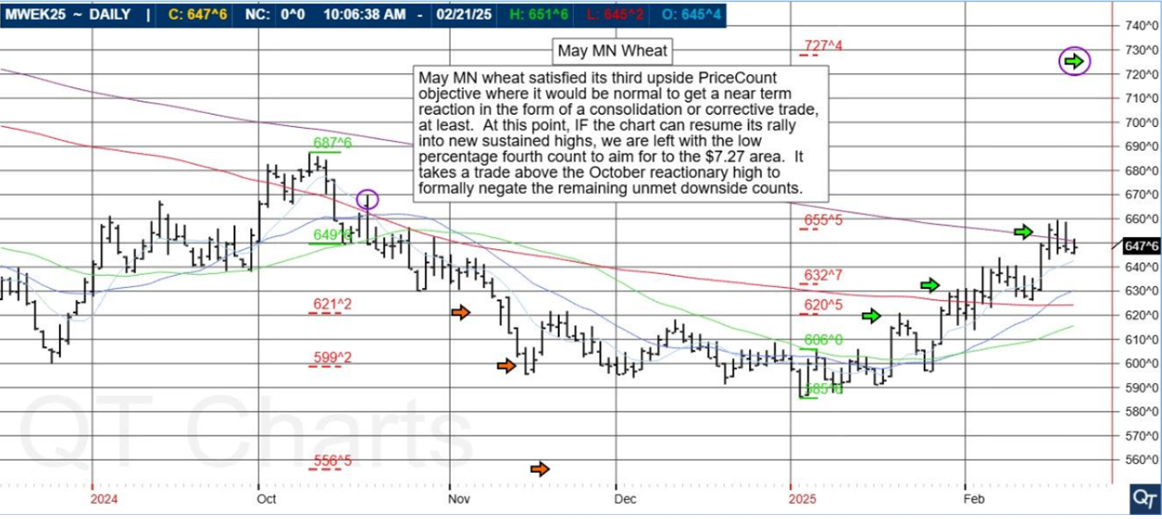
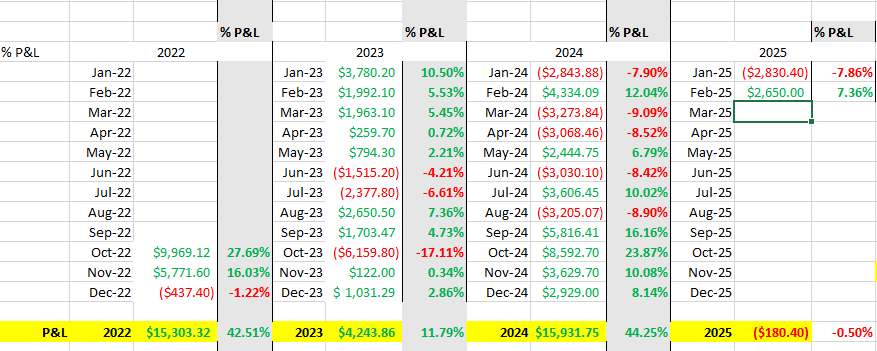
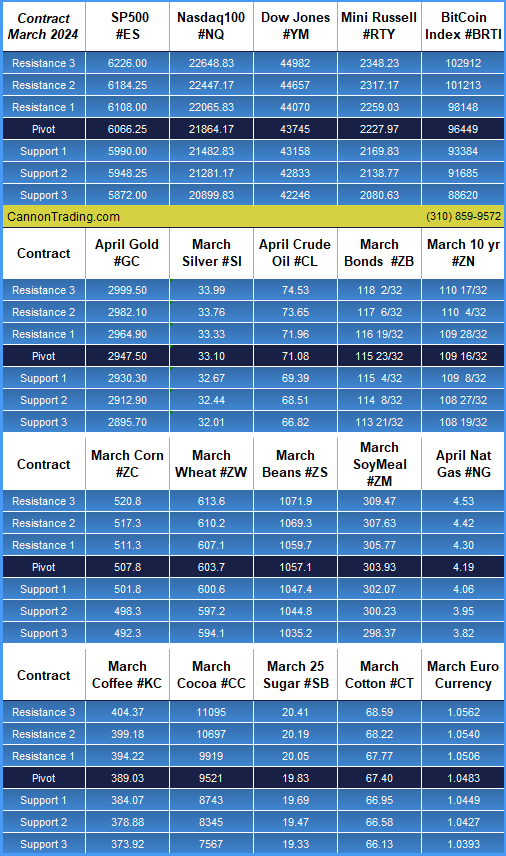
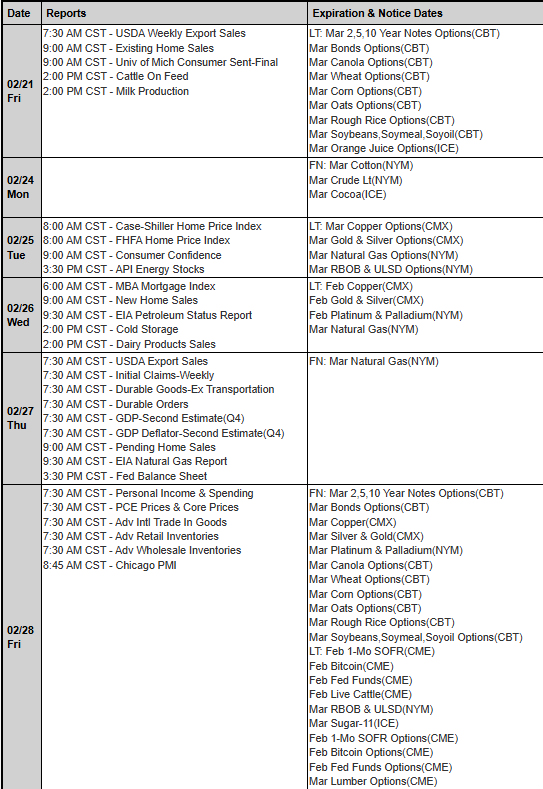
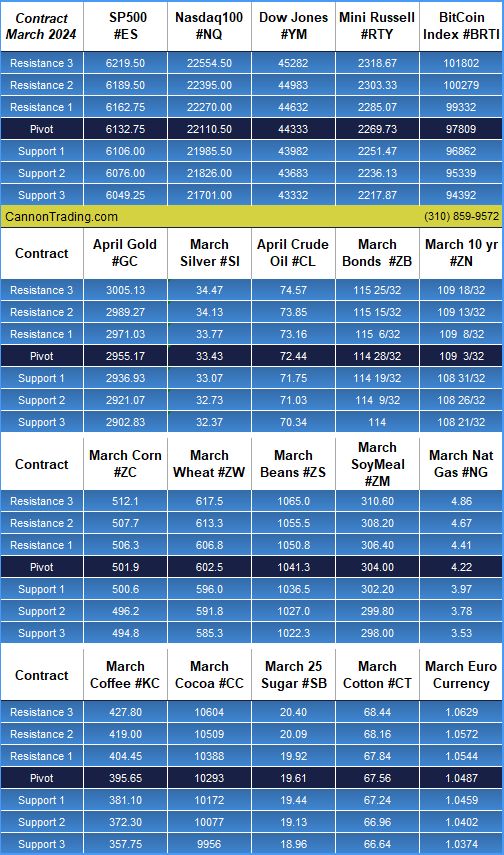
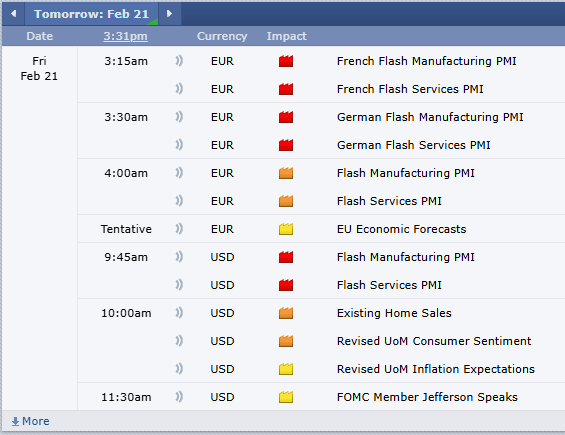
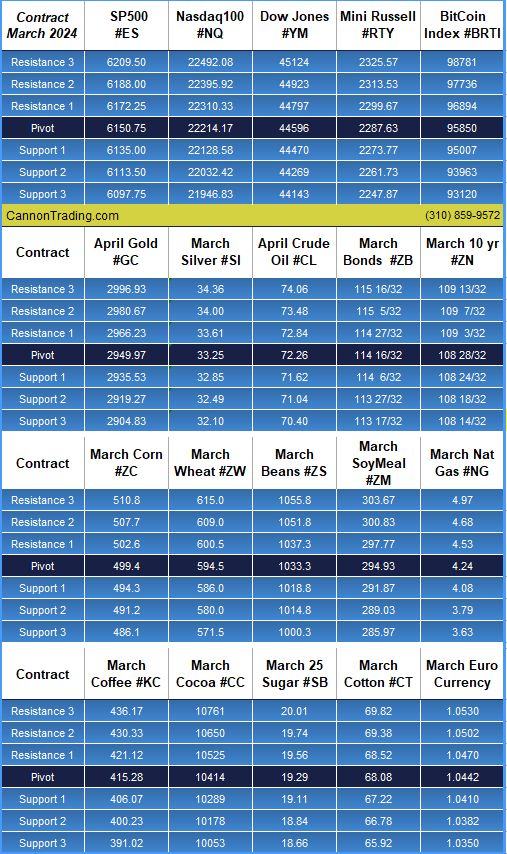
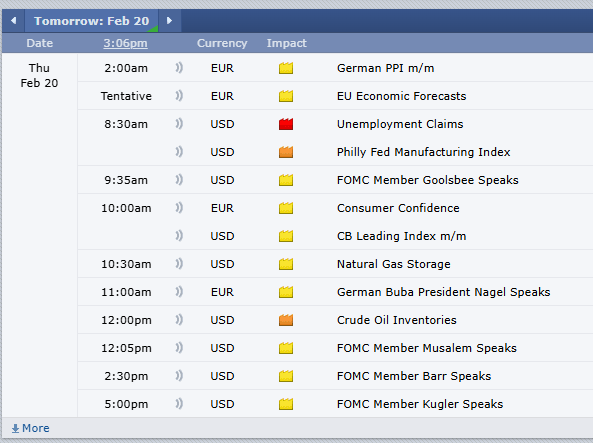
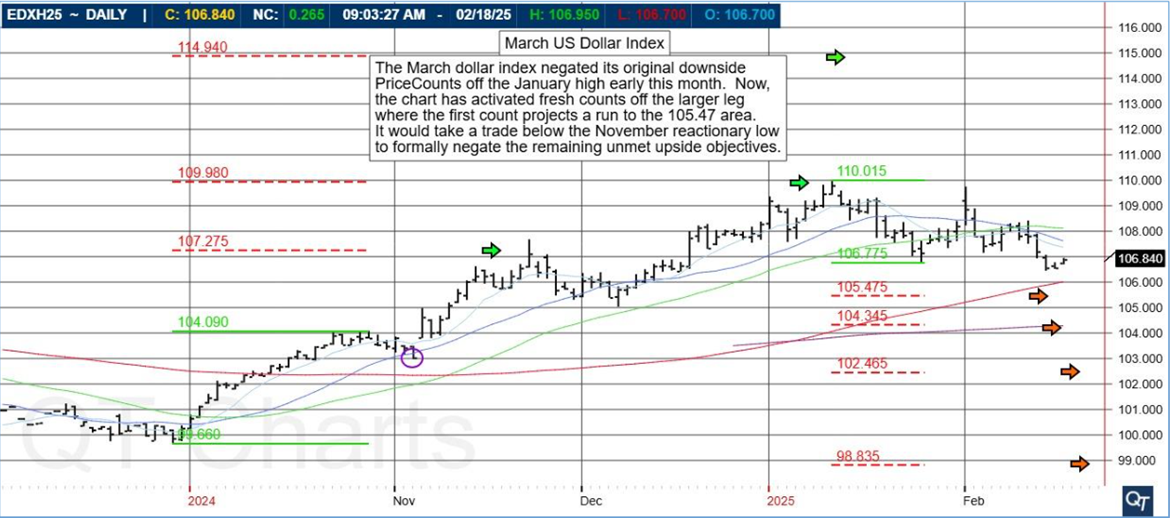
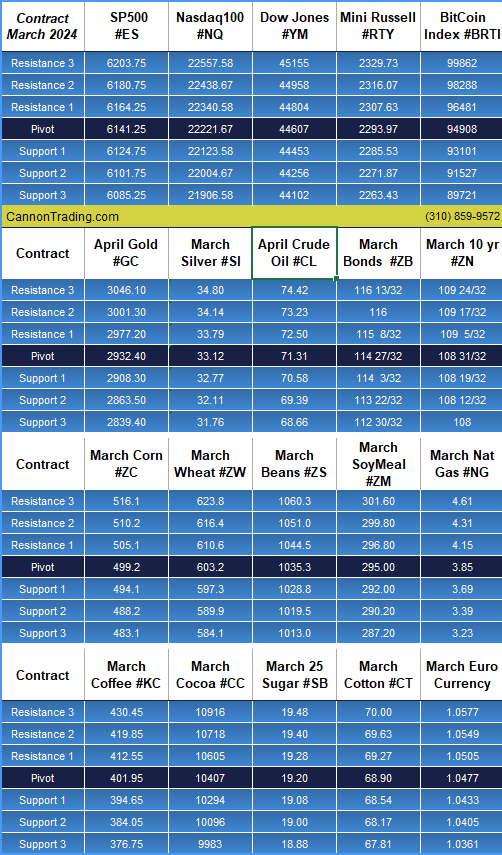
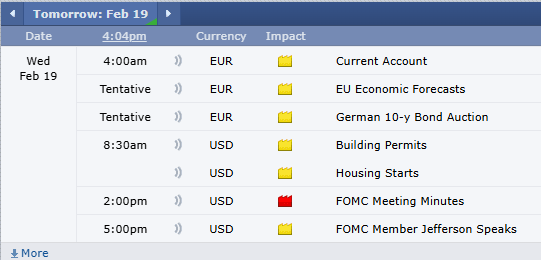
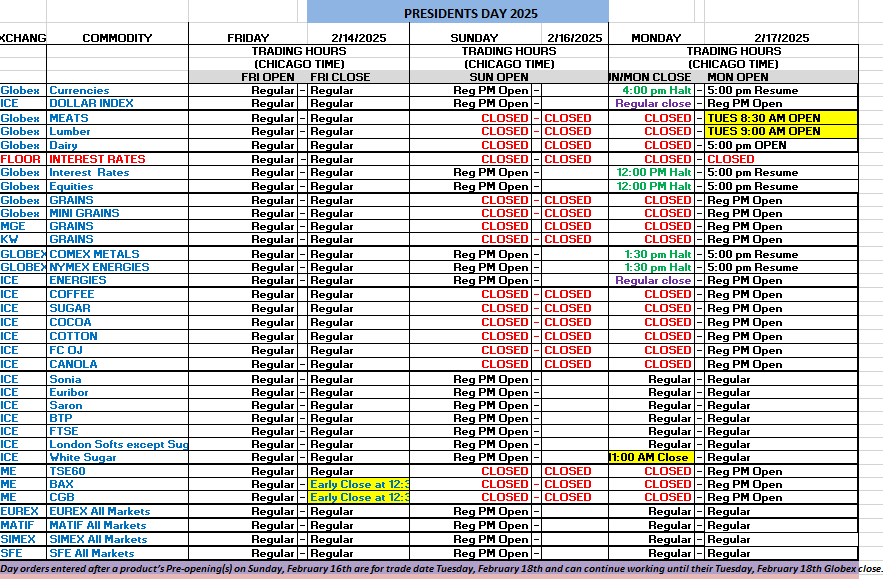
Platinum futures remain one of the most compelling precious metals contracts for traders looking to hedge risk, speculate on price movements, or diversify their portfolios. As 2025 unfolds, futures traders must equip themselves with the right knowledge, reports, and strategies to navigate the evolving market landscape. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the key factors influencing platinum futures, historical trends, and why Cannon Trading Company is an ideal futures trading broker for traders of all experience levels.
10 Tips and Pointers for Trading Platinum Futures in 2025
- Understand Supply and Demand Dynamics
The price of platinum futures is heavily influenced by supply and demand. South Africa and Russia dominate global platinum production, meaning any geopolitical instability, labor strikes, or production halts in these regions can significantly impact futures contract trading.
- Follow Automotive Industry Trends
Platinum is widely used in catalytic converters for vehicles. Any regulatory changes related to emission standards, shifts in electric vehicle (EV) adoption, or automotive production trends can influence platinum futures prices.
- Monitor Interest Rates and Inflation
Precious metals, including platinum, often act as a hedge against inflation. With potential shifts in Federal Reserve policies, traders must watch interest rate decisions closely, as they impact investor sentiment toward precious metals.
- Track Global Economic Growth
Platinum is an industrial metal, meaning global economic growth can affect demand. Rising manufacturing activity and GDP growth often correlate with increased platinum consumption, impacting futures contract trading.
- Study Historical Platinum Futures Trends
Historically, platinum has exhibited high volatility compared to gold and silver. Futures traders should analyze past market cycles to identify patterns that may help them predict price movements in 2025.
- Consider Seasonal Trends
Like other commodities, platinum has seasonal price tendencies. Historically, platinum prices tend to rise in the first quarter due to increased industrial activity after the holiday season.
- Leverage Technical Analysis
Using technical indicators like moving averages, RSI, and Fibonacci retracements can help futures traders time their platinum futures trades more effectively.
- Stay Updated on Mining Reports
Major mining reports from companies such as Anglo-American Platinum and Impala Platinum Holdings provide insights into production levels and potential supply shortages that can impact futures contract trading.
- Hedge with Options and Spread Strategies
To manage risk, futures traders can utilize option contracts and spread strategies when trading platinum futures. Spreads, such as bull call spreads, can provide downside protection while allowing participation in potential upside movement.
- Choose a Reliable Futures Trading Broker
Selecting a trustworthy broker is crucial for success in futures trading. Cannon Trading Company stands out due to its diverse trading platforms, top-tier regulatory reputation, and high customer satisfaction.
Trends to Expect in Platinum Futures and Corn Futures in 2025
Platinum futures are expected to be influenced by multiple key factors in 2025:
- Green Energy Transition: The hydrogen fuel cell industry, which uses platinum as a catalyst, is likely to see continued investment, increasing demand for the metal.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: As global supply chains continue to recover from the pandemic and geopolitical uncertainties, platinum availability may fluctuate.
- U.S. Dollar Strength: A stronger dollar typically pressures platinum prices downward, while a weaker dollar can support price gains.
- Federal Reserve Policies: Interest rate cuts could drive investment in precious metals, benefiting platinum futures traders.
Meanwhile, corn futures are expected to experience volatility driven by:
- Weather Conditions: Droughts, floods, and unexpected weather events will impact supply and price movements.
- Export Demand: China and other major importers’ buying patterns will heavily influence price trends.
- Biofuel Policies: Corn is a primary component in ethanol production, and regulatory policies on biofuels can significantly impact futures trading.
Key Reports to Analyze Before Trading Platinum Futures
When assessing potential platinum futures trades, traders should monitor the following reports:
- Commitment of Traders (COT) Report: This report provides insight into the positions of institutional traders, helping traders gauge market sentiment.
- U.S. Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) Report: Employment data impacts inflation and economic growth projections, influencing platinum demand.
- Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) Statements: Interest rate decisions affect the attractiveness of precious metals.
- World Platinum Investment Council (WPIC) Reports: Provides insights into supply-demand forecasts for platinum.
- Auto Industry Production Reports: Key for understanding platinum demand from catalytic converter manufacturing.
Historical Trends in Platinum Futures and Other Precious Metals
Platinum has a unique history in the commodities market. Unlike gold and silver, which are primarily monetary metals, platinum has a more industrial focus. Some notable historical trends include:
- Early 2000s Boom: Platinum prices surged due to increasing demand from the auto industry and a weaker dollar.
- 2008 Financial Crisis: Prices crashed alongside other assets but rebounded as economic recovery began.
- 2010-2014 Rally: Strong industrial demand and investor interest pushed platinum to highs above $1,800 per ounce.
- 2015-2020 Decline: Rising palladium substitution in automotive applications and mining oversupply contributed to price stagnation.
- 2021-Present Recovery: Increased interest in green energy and supply chain disruptions have sparked renewed volatility.
Gold and silver futures have historically been more stable but still follow macroeconomic and geopolitical trends. Traders should compare these metals to platinum futures to identify relative value opportunities.
Why Cannon Trading Company is the Best Futures Trading Broker for Platinum Futures
For traders looking for a reliable futures broker, Cannon Trading Company stands out for several reasons:
- Wide Selection of Free Trading Platforms: Cannon offers top-tier platforms such as E-Futures International, CQG, and Trade Navigator, providing traders with excellent execution speed and analytical tools.
- Decades of Experience: Established in 1988, Cannon Trading has a long-standing reputation for integrity and service excellence in the futures trading industry.
- 5-Star TrustPilot Ratings: With consistently high ratings from satisfied clients, Cannon Trading provides excellent customer support and trading guidance.
- Regulatory Compliance: As a member of the National Futures Association (NFA) and Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), Cannon upholds the highest industry standards for transparency and security.
- Personalized Service: Whether you’re a novice or experienced trader, Cannon Trading offers tailored solutions to fit your trading style and risk tolerance.
If you’re serious about trading platinum futures, choosing a seasoned futures trading broker like Cannon Trading Company ensures you have the best tools, support, and expertise at your disposal.
Trading platinum futures in 2025 requires a deep understanding of market fundamentals, technical strategies, and macroeconomic influences. By following key reports, monitoring industrial demand, and leveraging expert futures brokers like Cannon Trading Company, traders can position themselves for success in the evolving futures trading landscape.
For more information, click here.
Ready to start trading futures? Call us at 1(800)454-9572 – Int’l (310)859-9572 (International), or email info@cannontrading.com to speak with one of our experienced, Series-3 licensed futures brokers and begin your futures trading journey with Cannon Trading Company today.
Disclaimer: Trading Futures, Options on Futures, and retail off-exchange foreign currency transactions involve substantial risk of loss and are not suitable for all investors. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Carefully consider if trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances, knowledge, and financial resources. You may lose all or more of your initial investment. Opinions, market data, and recommendations are subject to change at any time.
Important: Trading commodity futures and options involves a substantial risk of loss. The recommendations contained in this article are opinions only and do not guarantee any profits. This article is for educational purposes. Past performances are not necessarily indicative of future results.
This article has been generated with the help of AI Technology and modified for accuracy and compliance.
Follow us on all socials: @cannontrading