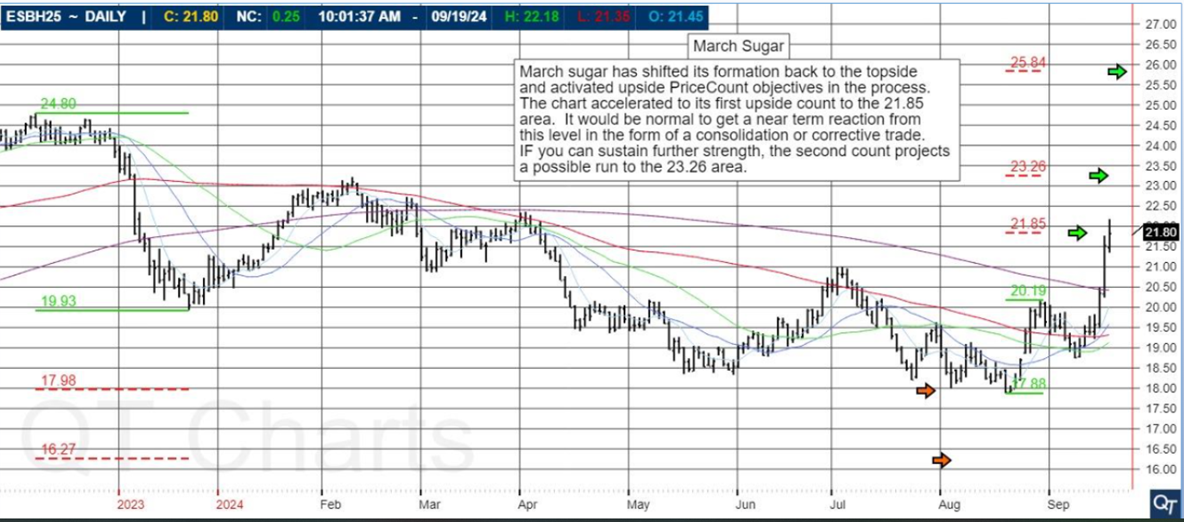
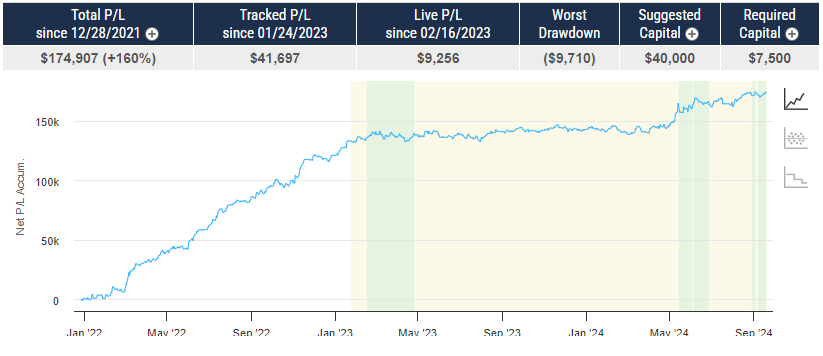
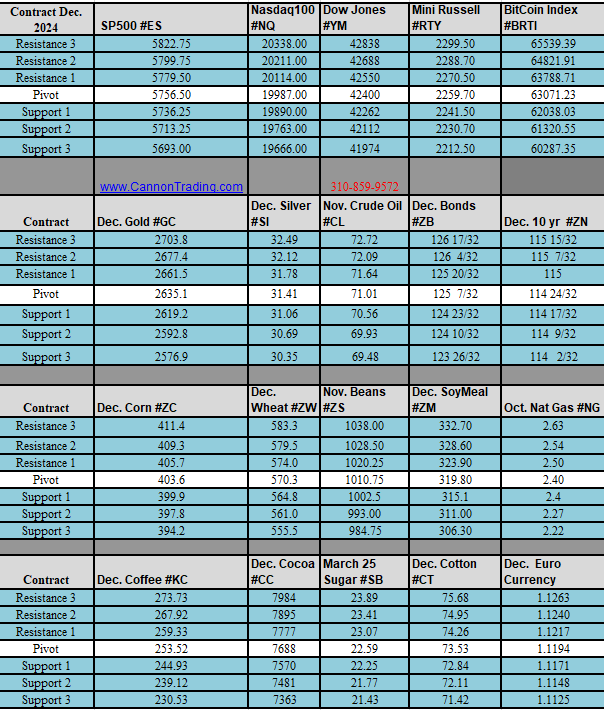
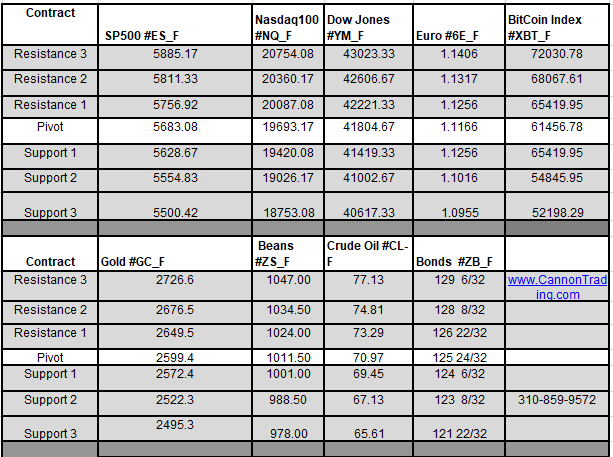
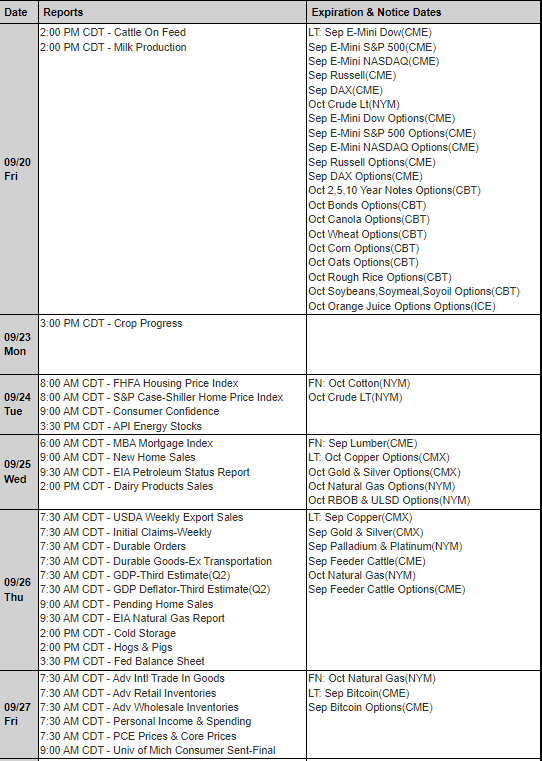
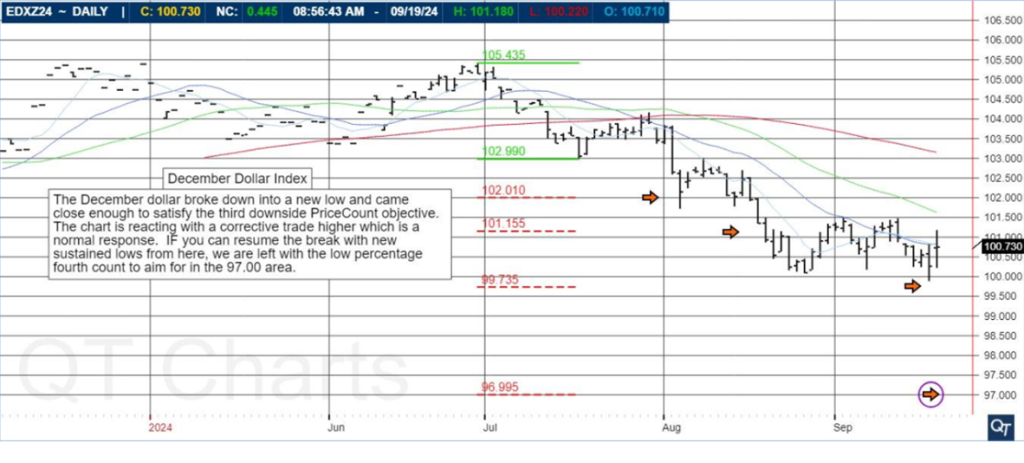
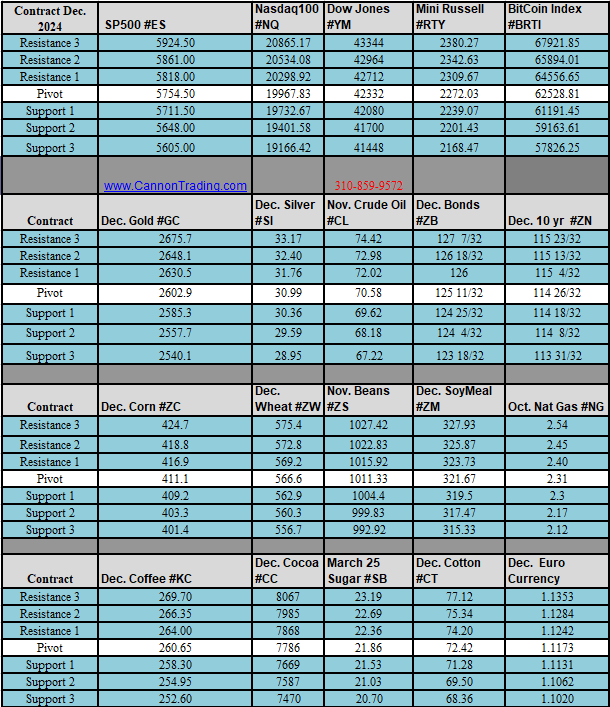
What are S&P 500 Index Futures?
S&P 500 Index Futures are standardized contracts traded on futures exchanges that allow traders to speculate on the future value of the S&P 500 Index, a widely followed benchmark representing 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States. These futures are among the most liquid and widely traded financial derivatives globally, making them a crucial tool for both hedgers and speculators in the financial markets.

The S&P 500 Index Futures, commonly referred to as SPX Index Futures, provide investors with a way to gain exposure to the overall U.S. equity market without needing to buy individual stocks. This contract derives its value from the S&P 500 Index, which tracks the performance of these large-cap companies. As such, SP500 Index Futures are not just popular among institutional investors but also among individual traders looking to capitalize on movements in the broader stock market.
Key Features of S&P 500 Index Futures Contracts
1. Contract Specifications
- Underlying Asset: The underlying asset of an S&P 500 Index Future is the S&P 500 Index itself. The value of the contract is tied to the performance of this index.
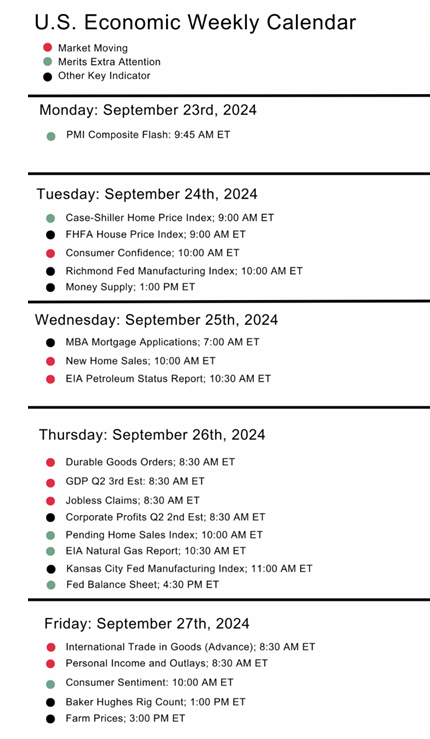
- Contract Size: The standard contract size for S&P 500 Index Futures is $250 multiplied by the value of the S&P 500 Index. For example, if the S&P 500 Index is trading at 4,000, the value of one futures contract would be $1,000,000 ($250 x 4,000).
- E-mini Contracts: Due to the large size of the standard S&P 500 futures contract, E-mini S&P 500 futures were introduced. These contracts are one-fifth the size of the standard contract, with a value of $50 multiplied by the index. E-minis have become more popular due to their affordability and accessibility.
- Tick Size: The minimum price movement, or tick size, for the standard S&P 500 futures contract is 0.25 index points, which equals $12.50 per contract. For E-mini contracts, the tick size is also 0.25 index points, but it equals $12.50 due to the smaller contract size.
- Expiration: S&P 500 Index Futures have a quarterly expiration cycle, typically expiring in March, June, September, and December. The contracts are settled in cash, meaning there is no delivery of the underlying asset, just a cash payment based on the contract’s final settlement price.
2. S&P 500 Futures Trading – Trading Hours
S&P 500 Index Futures are traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and are available for trading nearly 24 hours a day during the trading week. This extended trading period allows market participants to react to global events that occur outside of regular U.S. market hours, providing continuous opportunities for trading.
3. Leverage
One of the most significant advantages of trading S&P 500 Index Futures is the ability to use leverage. Leverage allows traders to control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital. However, while leverage can magnify profits, it can also amplify losses, making it a double-edged sword that requires careful risk management.
4. Margin Requirements
To trade S&P 500 Index Futures, traders must post a margin, which is a percentage of the contract’s total value. The initial margin is the amount required to open a position, while the maintenance margin is the minimum balance that must be maintained in the account to keep the position open. If the account balance falls below the maintenance margin, the trader must deposit additional funds to bring the balance back up to the required level.
5. Hedging and Speculation
S&P 500 Index Futures are used for both hedging and speculative purposes. Hedgers, such as institutional investors or portfolio managers, use these futures to protect against potential losses in their equity portfolios. For instance, if a portfolio manager anticipates a decline in the stock market, they can sell S&P 500 futures to offset potential losses in their holdings.
Speculators, on the other hand, use S&P 500 futures to profit from anticipated market movements. By taking a long or short position, speculators can capitalize on price changes in the S&P 500 Index without having to invest in the underlying stocks.
6. Settlement
S&P 500 Index Futures are cash-settled, meaning that at expiration, the contracts are settled based on the difference between the contract price and the final settlement price of the S&P 500 Index. Traders who hold positions until expiration will either receive or pay the difference in cash, depending on whether they were long or short on the contract.
Trading Strategies Using S&P 500 Index Futures
1. Directional Trading
Directional trading involves taking a position based on the expectation of a future price movement in the S&P 500 Index. If a trader believes the market will rise, they can buy (go long) S&P 500 Index Futures. Conversely, if they anticipate a decline, they can sell (go short) the futures contract. This strategy is straightforward but requires a strong understanding of market trends and economic indicators that can influence the index.
2. Hedging
Hedging with S&P 500 Index Futures is a common strategy for reducing the risk of adverse price movements in an equity portfolio. For example, a portfolio manager who holds a diversified portfolio of U.S. stocks can sell S&P 500 futures contracts to protect against a potential decline in the market. If the market does fall, the losses in the portfolio may be offset by gains in the futures position.
3. Spread Trading
Spread trading involves taking simultaneous long and short positions in related futures contracts to profit from the price difference between them. In the context of S&P 500 Index Futures, traders might engage in calendar spreads, where they buy and sell contracts with different expiration dates, aiming to profit from changes in the price difference as the contracts approach expiration.
5. Arbitrage
Arbitrage opportunities in S&P 500 Index Futures arise when the futures price deviates significantly from the fair value of the underlying index. Traders can exploit these discrepancies by buying or selling the index and taking the opposite position in the futures market, locking in a risk-free profit. However, true arbitrage opportunities are rare and typically short-lived, requiring swift action and large capital.
The Role of Futures Brokers in Trading S&P 500 Index Futures
Futures brokers play a critical role in facilitating the trading of S&P 500 Index Futures. They provide access to the futures markets, offer trading platforms, execute orders, and often provide valuable research and market analysis to help traders make informed decisions.
Choosing a Futures Broker
Selecting the right futures broker is crucial for success in trading S&P 500 Index Futures. A good futures broker will offer competitive pricing, a robust trading platform, and excellent customer service. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a futures broker:
- Experience and Reputation: Look for a broker with a long-standing reputation in the industry. Experienced brokers are more likely to provide reliable services and understand the intricacies of futures trading.
- Trading Platform: The broker’s trading platform should be user-friendly, with advanced charting tools, real-time data, and quick order execution. A good platform can make a significant difference in a trader’s ability to react swiftly to market changes.
- Commission and Fees: Compare the commission rates and fees charged by different brokers. While cost should not be the only factor, finding a broker with competitive pricing can help maximize profits.
- Customer Support: Excellent customer support is essential, especially for new traders who may need assistance navigating the futures markets. A broker that offers 24/7 support can be invaluable in addressing issues as they arise.
- Educational Resources: Many brokers offer educational resources, including webinars, articles, and one-on-one coaching. These resources can be particularly beneficial for traders who are new to futures trading.
Cannon Trading: A Trusted Partner for S&P 500 Index Futures Trading
Cannon Trading is one such futures broker known for its deep industry experience and commitment to helping traders succeed. With over three decades of experience in the futures industry, Cannon Trading has established itself as a reliable partner for both novice and experienced traders.
- Seasoned Brokers: Cannon Trading boasts a team of seasoned brokers who are well-versed in the complexities of futures trading. These professionals can provide personalized guidance, helping traders understand the nuances of S&P 500 Index Futures and develop effective trading strategies.
- Advanced Trading Platforms: Cannon Trading offers access to advanced trading platforms that cater to the needs of different types of traders. Whether you prefer a desktop application, web-based trading, or mobile access, Cannon Trading has the tools to support your trading style.
- Comprehensive Market Research: Staying informed about market developments is crucial in futures trading. Cannon Trading provides clients with access to comprehensive market research, including daily reports, technical analysis, and expert insights, helping traders stay ahead of market trends.
- Risk Management Tools: Managing risk is a fundamental aspect of successful futures trading. Cannon Trading offers various risk management tools, including stop-loss orders and automated trading strategies, to help traders protect their investments.
- Educational Support: For traders looking to deepen their knowledge of futures markets, Cannon Trading offers a wealth of educational resources. From webinars and articles to one-on-one coaching sessions, traders can access the information they need to improve their trading skills.
Understanding the Risks of Trading S&P 500 Index Futures
While trading S&P 500 Index Futures offers significant profit potential, it also comes with inherent risks. It is essential for traders to understand these risks and develop strategies to manage them effectively.
1. Market Risk
Market risk refers to the potential for losses due to adverse price movements in the S&P 500 Index. Because futures contracts are leveraged, even small price changes can result in substantial gains or losses. Traders must be prepared for the possibility of significant volatility and should consider using stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
2. Leverage Risk
Leverage magnifies both profits and losses in futures trading. While it allows traders to control large positions with a small amount of capital, it also increases the potential for substantial losses if the market moves against the trader. Understanding the implications of leverage and using it judiciously is critical for long-term success.
3. Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk arises when there is insufficient market activity to execute trades at the desired price. While S&P 500 Index Futures are generally highly liquid, there may be times when market liquidity is lower, particularly during off-hours or periods of extreme market stress. Traders should be aware of this risk and avoid placing large orders during illiquid periods.
4. Counterparty Risk
In futures trading, counterparty risk is mitigated by the futures exchange, which acts as the counterparty to all trades. However, traders should still be aware of the financial stability of their futures broker, as a broker’s insolvency could result in the loss of funds.
S&P 500 Index Futures are a powerful tool for traders and investors looking to gain exposure to the U.S. stock market. These futures contracts offer numerous advantages, including leverage, liquidity, and the ability to hedge against market risk. However, they also come with significant risks that require careful management.
Futures brokers like Cannon Trading play a vital role in helping traders navigate the complexities of the futures markets. With their extensive experience, advanced trading platforms, and commitment to client education, brokers like Cannon Trading can provide the support and resources needed to succeed in trading S&P 500 Index Futures.
Whether you are a seasoned trader or new to the world of futures, understanding the intricacies of S&P 500 Index Futures and working with a trusted broker can help you achieve your financial goals. With the right knowledge, tools, and support, the opportunities in S&P 500 Index Futures trading are vast, offering the potential for significant returns in the dynamic world of financial markets.
For more information, click here.
Ready to start trading futures? Call us at 1(800)454-9572 (US) or (310)859-9572 (International), or email info@cannontrading.com to speak with one of our experienced, Series-3 licensed futures brokers and begin your futures trading journey with E-Futures.com today.
Disclaimer: Trading Futures, Options on Futures, and retail off-exchange foreign currency transactions involve substantial risk of loss and are not suitable for all investors. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Carefully consider if trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances, knowledge, and financial resources. You may lose all or more of your initial investment. Opinions, market data, and recommendations are subject to change at any time.
Important: Trading commodity futures and options involves a substantial risk of loss. The recommendations contained in this article are opinions only and do not guarantee any profits. This article is for educational purposes. Past performances are not necessarily indicative of future results.
This article has been generated with the help of AI Technology and modified for accuracy and compliance.
Follow us on all socials: @cannontrading